Art Activity Structural Features During Week 5 of Fetal Development
Chapter 24. Animal Reproduction and Development
24.5. Human Pregnancy and Birth
Learning Objectives
By the stop of this department, you lot volition exist able to:
- Explain fetal development during the 3 trimesters of gestation
- Describe labor and delivery
- Compare the efficacy and duration of various types of contraception
- Hash out causes of infertility and the therapeutic options available
Pregnancy begins with the fertilization of an egg and continues through to the birth of the individual. The length of time of gestation varies amid animals, only is very similar among the great apes: human gestation is 266 days, while chimpanzee gestation is 237 days, a gorilla'south is 257 days, and orangutan gestation is 260 days long. The fox has a 57-twenty-four hours gestation. Dogs and cats have like gestations averaging 60 days. The longest gestation for a land mammal is an African elephant at 640 days. The longest gestations among marine mammals are the beluga and sperm whales at 460 days.
Man Gestation
Day before fertilization, the egg has finished meiosis and becomes a mature oocyte. When fertilized (at formulation) the egg becomes known as a zygote. The zygote travels through the oviduct to the uterus (Figure 24.eighteen). The developing embryo must implant into the wall of the uterus within seven days, or it volition deteriorate and die. The outer layers of the zygote (blastocyst) grow into the endometrium by digesting the endometrial cells, and wound healing of the endometrium closes upwards the blastocyst into the tissue. Another layer of the blastocyst, the chorion, begins releasing a hormone called human being beta chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG) which makes its way to the corpus luteum and keeps that structure active. This ensures acceptable levels of progesterone that volition maintain the endometrium of the uterus for the back up of the developing embryo. Pregnancy tests make up one's mind the level of β -HCG in urine or serum. If the hormone is nowadays, the test is positive.
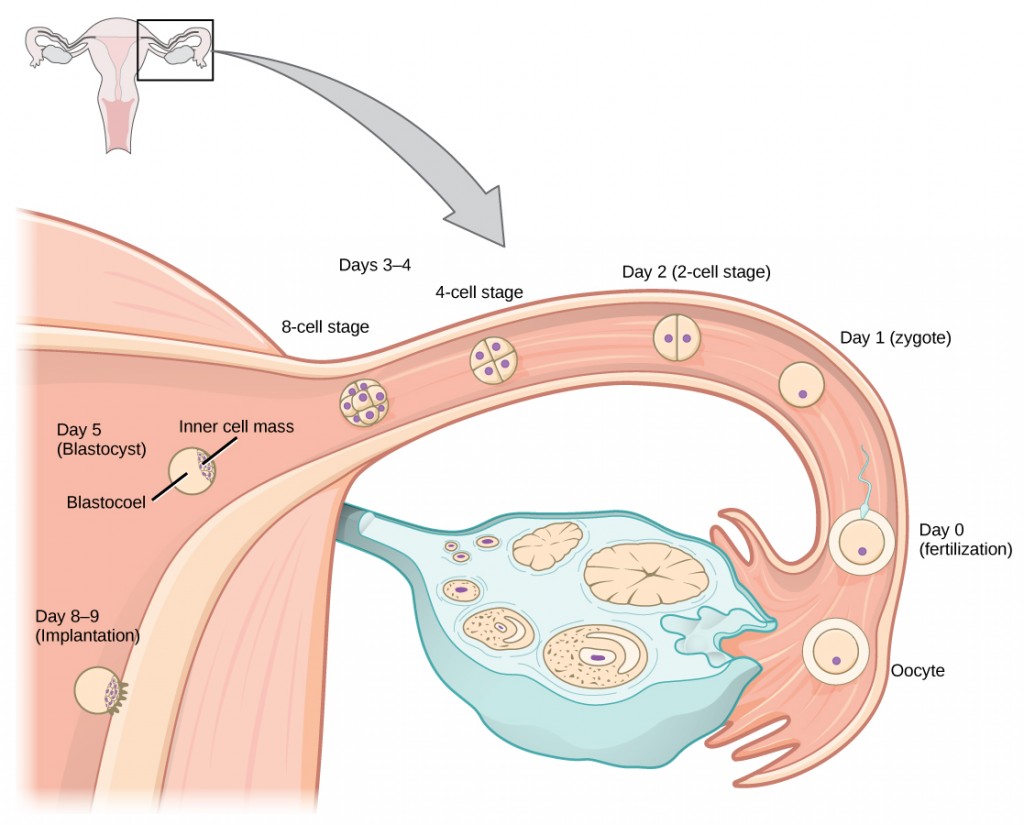
The gestation period is divided into three equal periods or trimesters. During the first two to four weeks of the first trimester, nutrition and waste are handled by the endometrial lining through diffusion. As the trimester progresses, the outer layer of the embryo begins to merge with the endometrium, and the placenta forms. This organ takes over the nutrient and waste product requirements of the embryo and fetus, with the mother'south blood passing nutrients to the placenta and removing waste from it. Chemicals from the fetus, such as bilirubin, are candy by the female parent's liver for elimination. Some of the mother's immunoglobulins will pass through the placenta, providing passive immunity confronting some potential infections.
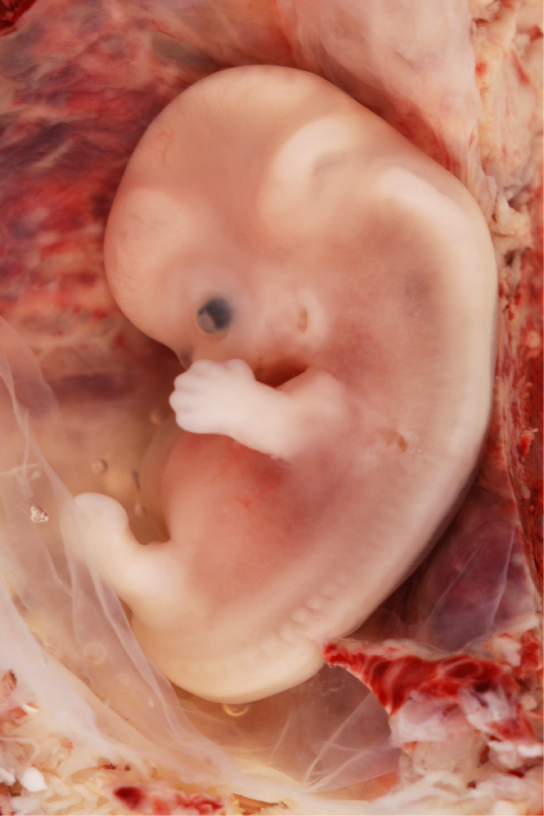
Internal organs and body structures begin to develop during the first trimester. By five weeks, limb buds, eyes, the center, and liver have been basically formed. By viii weeks, the term fetus applies, and the body is essentially formed, as shown in Figure 24.19. The individual is well-nigh five centimeters (two inches) in length and many of the organs, such as the lungs and liver, are not withal operation. Exposure to whatever toxins is specially dangerous during the first trimester, as all of the torso'southward organs and structures are going through initial development. Anything that affects that development can take a severe effect on the fetus' survival.
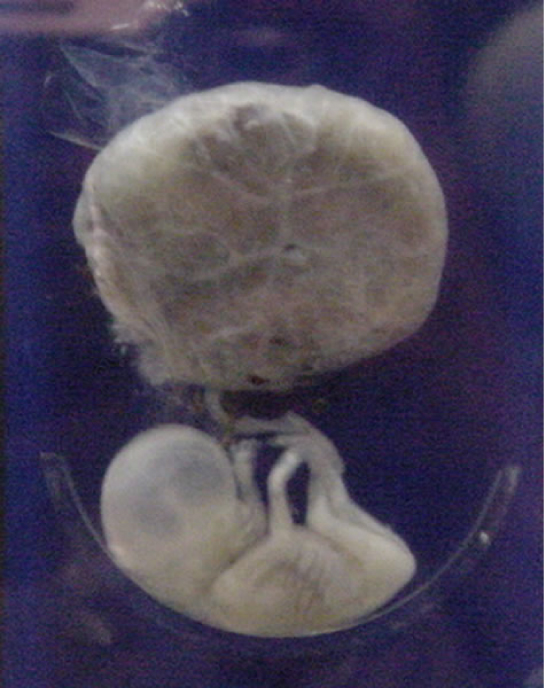
During the second trimester, the fetus grows to about xxx cm (12 inches), as shown in Figure 24.xx. It becomes active and the mother usually feels the first movements. All organs and structures continue to develop. The placenta has taken over the functions of diet and waste and the production of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum, which has degenerated. The placenta will continue performance up through the delivery of the baby.
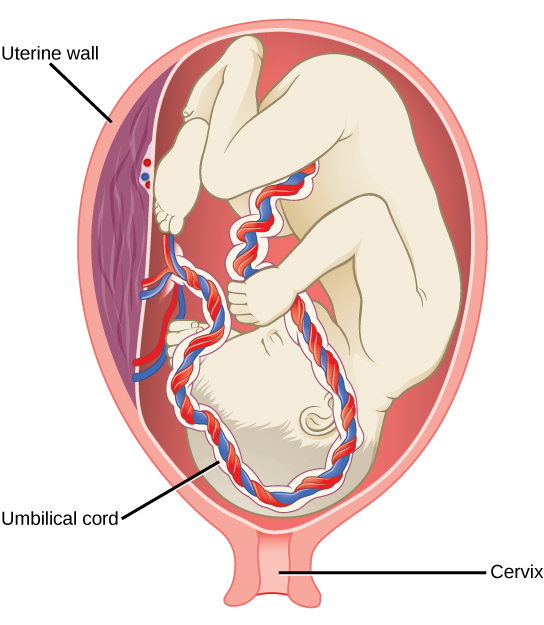
During the third trimester, the fetus grows to three to 4 kg (vi ½ -8 ½ lbs.) and well-nigh 50 cm (19-20 inches) long, as illustrated in Effigy 24.21. This is the period of the most rapid growth during the pregnancy. Organ development continues to birth (and some systems, such as the nervous system and liver, go along to develop after birth). The female parent will be at her near uncomfortable during this trimester. She may urinate frequently due to pressure on the float from the fetus. There may also be abdominal blockage and circulatory bug, especially in her legs. Clots may class in her legs due to pressure level from the fetus on returning veins equally they enter the abdominal cavity.
Concept in Activity

Visit this site to meet the stages of human fetal development.
Labor and Nascency
Labor is the concrete efforts of expulsion of the fetus and the placenta from the uterus during nascence (parturition). Toward the end of the third trimester, estrogen causes receptors on the uterine wall to develop and bind the hormone oxytocin. At this fourth dimension, the baby reorients, facing frontward and down with the back or crown of the head engaging the cervix (uterine opening). This causes the cervix to stretch and nerve impulses are sent to the hypothalamus, which signals for the release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary. The oxytocin causes the smooth muscle in the uterine wall to contract. At the same fourth dimension, the placenta releases prostaglandins into the uterus, increasing the contractions. A positive feedback relay occurs between the uterus, hypothalamus, and the posterior pituitary to assure an adequate supply of oxytocin. As more than smooth muscle cells are recruited, the contractions increase in intensity and strength.
There are 3 stages to labor. During stage 1, the cervix thins and dilates. This is necessary for the baby and placenta to be expelled during birth. The cervix will somewhen amplify to about 10 cm. During stage two, the infant is expelled from the uterus. The uterus contracts and the mother pushes as she compresses her abdominal muscles to aid the delivery. The last stage is the passage of the placenta afterward the baby has been built-in and the organ has completely disengaged from the uterine wall. If labor should finish before stage two is reached, synthetic oxytocin, known as Pitocin, can be administered to restart and maintain labor.
An alternative to labor and commitment is the surgical delivery of the baby through a procedure called a Caesarian section. This is major abdominal surgery and can lead to post-surgical complications for the mother, just in some cases it may exist the only way to safely evangelize the infant.
The female parent'due south mammary glands go through changes during the third trimester to prepare for lactation and breastfeeding. When the baby begins suckling at the chest, signals are sent to the hypothalamus causing the release of prolactin from the inductive pituitary. Prolactin causes the mammary glands to produce milk. Oxytocin is also released, promoting the release of the milk. The milk contains nutrients for the infant's development and growth as well every bit immunoglobulins to protect the child from bacterial and viral infections.
Contraception and Birth Control
The prevention of a pregnancy comes under the terms contraception or nascence control. Strictly speaking, contraception refers to preventing the sperm and egg from joining. Both terms are, all the same, frequently used interchangeably.
| Method | Examples | Failure Rate in Typical Use Over 12 Months |
|---|---|---|
| Barrier | male condom, female person condom, sponge, cervical cap, diaphragm, spermicides | xv to 24% |
| Hormonal | oral, patch, vaginal ring | eight% |
| injection | iii% | |
| implant | less than 1% | |
| Other | natural family planning | 12 to 25% |
| withdrawal | 27% | |
| sterilization | less than one% |
Tabular array 24.3 lists common methods of contraception. The failure rates listed are not the ideal rates that could be realized, just the typical rates that occur. A failure charge per unit is the number of pregnancies resulting from the method's utilise over a twelve-calendar month period. Bulwark methods, such as condoms, cervical caps, and diaphragms, block sperm from entering the uterus, preventing fertilization. Spermicides are chemicals that are placed in the vagina that kill sperm. Sponges, which are saturated with spermicides, are placed in the vagina at the cervical opening. Combinations of spermicidal chemicals and barrier methods achieve lower failure rates than practice the methods when used separately.
Nearly a quarter of the couples using barrier methods, natural family planning, or withdrawal tin look a failure of the method. Natural family unit planning is based on the monitoring of the menstrual wheel and having intercourse only during times when the egg is not available. A adult female's body temperature may rise a degree Celsius at ovulation and the cervical fungus may increase in volume and become more than pliable. These changes give a general indication of when intercourse is more than or less likely to effect in fertilization. Withdrawal involves the removal of the penis from the vagina during intercourse, before ejaculation occurs. This is a risky method with a high failure charge per unit due to the possible presence of sperm in the bulbourethral gland'south secretion, which may enter the vagina prior to removing the penis.
Hormonal methods use synthetic progesterone (sometimes in combination with estrogen), to inhibit the hypothalamus from releasing FSH or LH, and thus prevent an egg from being available for fertilization. The method of administering the hormone affects failure charge per unit. The most reliable method, with a failure rate of less than 1 percentage, is the implantation of the hormone under the skin. The aforementioned rate tin exist achieved through the sterilization procedures of vasectomy in the man or of tubal ligation in the woman, or by using an intrauterine device (IUD). IUDs are inserted into the uterus and establish an inflammatory condition that prevents fertilized eggs from implanting into the uterine wall.
Compliance with the contraceptive method is a stiff contributor to the success or failure rate of whatever particular method. The only method that is completely effective at preventing conception is abstinence. The pick of contraceptive method depends on the goals of the woman or couple. Tubal ligation and vasectomy are considered permanent prevention, while other methods are reversible and provide short-term contraception.
Termination of an existing pregnancy can be spontaneous or voluntary. Spontaneous termination is a miscarriage and commonly occurs very early in the pregnancy, usually within the first few weeks. This occurs when the fetus cannot develop properly and the gestation is naturally terminated. Voluntary termination of a pregnancy is an abortion. Laws regulating abortion vary between states and tend to view fetal viability equally the criteria for allowing or preventing the process.
Infertility
Infertility is the inability to conceive a child or carry a child to birth. About 75 percent of causes of infertility can be identified; these include diseases, such as sexually transmitted diseases that can cause scarring of the reproductive tubes in either men or women, or developmental issues frequently related to abnormal hormone levels in one of the individuals. Inadequate nutrition, especially starvation, can delay menstruation. Stress can too lead to infertility. Short-term stress can affect hormone levels, while long-term stress can delay puberty and cause less frequent menstrual cycles. Other factors that affect fertility include toxins (such as cadmium), tobacco smoking, marijuana use, gonadal injuries, and aging.
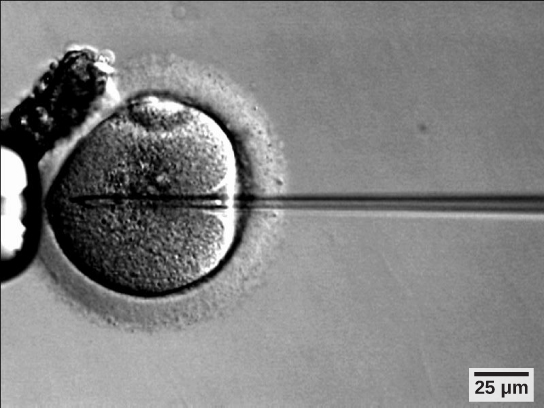
If infertility is identified, several assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are bachelor to aid conception. A common type of ART is in vitro fertilization (IVF) where an egg and sperm are combined outside the trunk and and then placed in the uterus. Eggs are obtained from the woman later extensive hormonal treatments that gear up mature eggs for fertilization and prepare the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg. Sperm are obtained from the man and they are combined with the eggs and supported through several cell divisions to ensure viability of the zygotes. When the embryos have reached the eight-jail cell phase, one or more is implanted into the woman'southward uterus. If fertilization is not accomplished by simple IVF, a procedure that injects the sperm into an egg can be used. This is chosen intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and is shown in Figure 24.22. IVF procedures produce a surplus of fertilized eggs and embryos that can be frozen and stored for time to come use. The procedures can also result in multiple births.
Summary
Human pregnancy begins with fertilization of an egg and proceeds through the three trimesters of gestation. The labor procedure has three stages (contractions, delivery of the fetus, expulsion of the placenta), each propelled past hormones. The start trimester lays down the basic structures of the body, including the limb buds, heart, eyes, and the liver. The 2d trimester continues the development of all of the organs and systems. The third trimester exhibits the greatest growth of the fetus and culminates in labor and delivery. Prevention of a pregnancy can be achieved through a diversity of methods including barriers, hormones, or other ways. Assisted reproductive technologies may help individuals who take infertility issues.
Exercises
- Nutrient and waste requirements for the developing fetus are handled during the first few weeks by:
- the placenta
- improvidence through the endometrium
- the chorion
- the blastocyst
- Progesterone is made during the third trimester by the:
- placenta
- endometrial lining
- chorion
- corpus luteum
- Which contraceptive method is 100 percentage effective at preventing pregnancy?
- prophylactic
- oral hormonal methods
- sterilization
- abstinence
- Which type of curt term contraceptive method is generally more constructive than others?
- barrier
- horomonal
- natural family planning
- withdrawal
- Which hormone is primarily responsible for the contractions during labor?
- oxytocin
- estrogen
- β -HCG
- progesterone
- Major organs begin to develop during which part of human being gestation?
- fertilization
- first trimester
- 2nd trimester
- third trimester
- Describe the major developments during each trimester of human being gestation.
- Describe the stages of labor.
Answers
- B
- A
- D
- B
- A
- B
- The start trimester lays downward the basic structures of the body, including the limb buds, heart, eyes, and the liver. The second trimester continues the development of all of the organs and systems established during the starting time trimester. The placenta takes over the production of estrogen and high levels of progesterone and handles the food and waste requirements of the fetus. The third trimester exhibits the greatest growth of the fetus, culminating in labor and delivery.
- Stage one of labor results in the thinning of the neck and the dilation of the cervical opening. Phase ii delivers the baby, and stage 3 delivers the placenta.
Glossary
contraception (also, birth control)
various means used to preclude pregnancy
gestation
length of time for fetal development to nascence
human beta chorionic gonadotropin ( β -HCG)
hormone produced by the chorion of the zygote that helps to maintain the corpus luteum and elevated levels of progesterone
infertility
disability to conceive, acquit, and deliver children
placenta
organ that supports the diffusion of nutrients and waste material between the mother's and fetus' blood
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/24-5-human-pregnancy-and-birth/
0 Response to "Art Activity Structural Features During Week 5 of Fetal Development"
Post a Comment